
July 18, 2025 ⏱️ 8 min
By Andrei N. & RnD Group
Can you imagine your machines having the power to warn you before they fail? Can you imagine a factory floor that constantly fine-tunes itself, optimizing every process in real time?
This is neither fiction nor the future — it is the present, and it is what Azure IoT makes possible today. Thus, in the following lines, we are going to deep dive into how Azure IoT can help you achieve all of these goals.
From Vision to Action
Whether we talk about manufacturing plants, warehouses, energy grids or other smart equipment, Azure IoT and its additional tools help in transforming traditional operations into intelligent systems that are more efficient, secure, and data driven. From the smallest sensor to industrial-grade servers, nowadays Azure IoT can connect devices, gather real-time data, run AI at the edge, and integrate seamlessly with cloud analytics.
The result? First, it is lower downtime. Secondly, it is faster decision-making. Finally, it is predictive insights and a competitive edge that’s hard to match.
With Azure IoT, companies are not just adding technology — but they are bringing business intelligence where it matters the most: at the very edge of the operations.
Azure IoT
Azure IoT is a cloud platform from Microsoft used for connecting, managing, and monitoring physical devices (these could be machines, sensors, etc.) over the internet.
Azure IO consists in two services:
- Azure IoT Hub – the central cloud gateway for secure two-way communication between devices and the cloud.
- Azure IoT Central – a ready-made SaaS platform for quickly visualizing and managing devices without coding.
What can Azure IoT be used for:
- Collect real-time data from machines.
- Control devices remotely.
- Monitor health and performance.
- Send all data to the cloud for analytics and storage.
Azure IoT Edge
Azure IoT Edge is the edge computing extension of Azure IoT. It makes possible to run “cloud intelligence” directly on devices (even when offline!).
It facilitates deploying:
- AI/ML models
- Stream Analytics jobs
- Custom “business logic” in containers
- Azure services like Functions or SQL – right on the machine
IoT Edge can run on various types of hardware (e.g., industrial PCs, Azure Stack Edge, or Raspberry Pi) and consists of the following blocks:
- IoT Edge Runtime: Software that manages modules and communication
- IoT Edge Modules: Docker-style containers that run logic or ML models
- IoT Edge Hub: Acts like a local version of Azure IoT Hub, routing data and managing connectivity
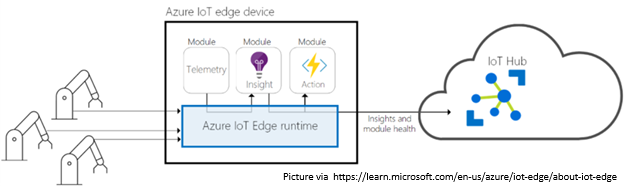
How They Work Together
To understand how Azure IoT and Azure IoT Edge can work together, we can make an analogy with something practical. Let us think of Azure IoT as a company’s headquarters, where strategy and coordination happen. In this case Azure IoT Edge would be like a branch office, where real-time work is happening, making decisions without always having to call HQ.
And here’s the flow:
-
- Azure IoT Hub (cloud) securely connects all devices, whether they’re sensors or edge gateways, etc.
- IoT Edge devices connect to IoT Hub just like regular devices—but they’re smarter.
- Deploy workloads from the cloud (e.g., ML models, analytics jobs) to the edge, via IoT Hub.
- The edge device runs the workloads itself, locally, and then processes data in real time.
- The edge device sends only relevant insights back to Azure.
- Azure then stores, analyzes, or displays data using services like Power BI, Azure Digital Twins, or Azure Machine Learning.
Extra Tooling
While Azure IoT comes with a powerful foundation for connecting and managing devices, real-world IoT solutions often need more than just connectivity between devices. To build smarter, safer, and more complex applications, Azure offers additional tools that extend the platform’s capabilities.
In this regard, two key components are Azure Digital Twins and Azure Sphere. These add powerful layers of intelligence and security to any IoT ecosystem. Together, they enable deeper insights through virtual modeling and ensure end-to-end device protection.
Azure Digital Twins
Azure Digital Twins is a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) from Microsoft that allows building digital replicas of real-world environments (like buildings, factories, utilities, or even entire cities). These digital models facilitate simulation, monitorization and optimization of physical spaces in real-time, by connecting to IoT and other data sources.

Here are some key capabilities/features of Azure Digital Twins:
- Model the physical world – It is possible to define digital twins using a modeling language called DTDL (Digital Twins Definition Language). Also, it allows modeling physical entities (like rooms, elevators, machines), their relationships (e.g., “Room A is in Building X”), and properties (like temperature, status).
- Live Data Integration: Connect IoT devices and data sources to feed real-time telemetry into digital models.
- Contextual Insights: Understand how elements relate to each other spatially, logically, or hierarchically.
- Simulation & Prediction: Run simulations or apply analytics and AI to optimize performance, detect anomalies, or predict future states.
- Event-driven Architecture: React to changes in the system through event routing and integration with services like Azure Functions or Event Grid.
When it comes to some real-life use cases of Azure Digital Twin, here are a few examples:
- Digitally represent and manage complex physical environments
- Perform real-time monitoring and automated responses
- Run simulations or what-if analyses
- Enable predictive maintenance, occupancy tracking, energy optimization, etc.
Azure Sphere
In an increasingly connected world, IoT devices are prime targets for cyberattacks. That’s where Azure Sphere comes into play- it’s specifically designed to ensure security.
Azure Sphere is an end-to-end security platform designed by Microsoft to protect Internet-connected microcontroller (MCU) devices (from the silicon hardware to the cloud). It ensures that even the smallest IoT devices (like sensors, controllers, smart meters, or appliances) are secure by design and remain protected throughout their lifecycle.

Azure Sphere involves three main elements working together:
1. Azure Sphere-certified MCU (Microcontroller Unit) – a specially designed chip that includes:
- A built-in secure processing environment
- A security subsystem for cryptographic operations and secure boot
- Support for real-time and application-level code on separate cores
2. Azure Sphere OS – a custom Linux-based operating system that:
- Provides container-like isolation between components
- Includes built-in defense-in-depth mechanisms
- Ensures secure app execution and communication
3. Azure Sphere Security Service (cloud) – a cloud-based service that:
- Continuously monitors device health
- Provides over-the-air (OTA) updates
- Authenticates devices and detects potential security breaches
Bringing Intelligence to the Edge
The real power of Azure IoT is fully revealed when AI and Machine Learning are brought directly to the edge devices. This enables decisions to be made in real time, even without constant cloud access.
Why AI at the Edge?
In traditional IoT architectures, devices collect data and forward it directly to the cloud for analysis. But there are cases and industries where even milliseconds matter (like energy or the medical sector). With Azure IoT Edge, AI models care run locally, on the devices themselves. This allows systems to analyze, react, and adapt instantly, right when data is collected.
The process to make this possible is quite complex and involves several steps, as shown below. This is basically the workflow for AI/ML in Azure IoT:
-
- Train the Model in the Cloud – use Azure Machine Learning or other frameworks to train a model with historical or labeled data.
- Export the Model to a Container – convert the model to ONNX, TensorFlow, PyTorch, or another compatible format and then package it in a Docker container to run on IoT Edge.
- Deploy via Azure IoT Hub – use IoT Hub to deploy the containerized model to your IoT Edge devices (the model becomes part of an IoT Edge module).
- Run Inference at the Edge – the device uses real-time sensor data to make predictions, detect issues, or classify events locally. There is no need to send raw data to the cloud—only actionable results.
- Send Insights to the Cloud – allows controlling what data goes to Azure (optimized summaries, alerts, or aggregated statistics).
Here are some real-world examples/usages:
- Factories: An edge device runs a model that analyzes vibration data from motors to predict mechanical failure before it happens.
- Logistics: A camera runs a ML model to recognize license plates or detect tampering on shipments.
- Healthcare: A wearable with an Azure Sphere MCU detects anomalies in patient vitals and triggers alerts immediately without cloud delay.
- Agriculture: Edge devices process soil and climate data to decide local irrigation schedules using a regression model.
Bottom Line
The Azure IoT ecosystem becomes exponentially more powerful when combined with IoT Edge and machine learning + AI.
In this landscape, Azure IoT is the central nervous system of the architecture, managing and monitoring devices from the cloud. Azure IoT Edge is the local brain, empowering devices to act intelligently and making decisions close to where data is generated/gathered (without always calling home) through embedded AI and Machine Learning models.
This is not just the Internet of Things – it is the Intelligent Edge, powered by Azure.





